Secure Shell (SSH) is a UNIX-based command interface and protocol for securely getting access to a remote computer. SSH is actually a suite of three utilities - slogin, ssh, and scp - that are secure versions of the earlier UNIX utilities, rlogin, rsh, and rcp. SSH commands are encrypted and secure in several ways. Jul 31, 2019 Restart SSH Service Command The command to restart sshd are as follows (you must login as root user). You must run command as per your Linux distribution or Unix variant. CentOS / RHEL / Fedora / Redhat Linux Restart SSH. Oct 22, 2018 The ssh command tells your system to connect to another machine. The –t option forces the remote system to enter the command in a terminal. Replace user@server.com with the username @ server name that you want to restart. The sudo reboot command can be switched out for sudo shutdown and the above options above can be used.
- Restart Sshd Service Linux
- Restart Ssh Aix
- Restart Ssh Agent Mac
- Restart Ssh Ubuntu
- Restart Ssh Service Ubuntu
- Restart Ssh
SSH service by OpenSSH is normally provided by the sshd daemon. In most Unix-based operating systems the daemon process can be managed by systemd, System V. Init scripts or the service command.
You can use all three methods to manage your SSH server on most platforms. Common options include the ability to start, stop and restart the SSH. You can also view detailed status of the running sshd daemon and set to whether or not to automatically start sshd during system startup.
Sudo stop ssh sudo start ssh As it leverages upstart, this is The Best Way™ to do it, rather than using /etc/init.d/ssh, service, or invoking sshd directly. Make sure to run both commands; if you get an error on stop ssh, start ssh anyway and see what it says—the service could already be stopped. Try restart using the following command: sudo service ssh restart The private/public RSA SSH keys are located in /.ssh/idrsa and /.ssh/idrsa.pub, respectively. You can transfer the public key to another machine to connect to it through public key authentication.
| Method | Command |
|---|---|
| System V. Init scripts | /etc/init.d/ssh [start|restart|stop|status] |
| Systemd | systemctl [start|restart|stop|status|enable|disable] ssh |
| service command | service ssh [start|restart|stop|status] |
Some distributions use sshd instead of ssh as the name of their init script.
Steps to manage OpenSSH server from command line:
- Start SSH service using systemd.
- Configure SSH to automatically start during system boot.
- Configure SSH service to not automatically start during system boot.
- View SSH status using systemd.
Cloud architect by profession but always consider himself as a developer, entrepreneur and an opensource enthusiast.
Comment anonymously. Login not required.
Restart Sshd Service Linux
This chapter explains how to install Cygwin and start the SSH daemon on Microsoft Windows hosts. This chapter is applicable only when you want to install a Management Agent on a Microsoft Windows host, using the Add Host Targets Wizard or EM CLI. In particular, this chapter covers the following:
Important:
If you do not want to install Cygwin to deploy Management Agents on Microsoft Windows hosts using the Add Host Targets Wizard or EM CLI, you can choose to deploy Management Agents on these hosts using the PsExec process utility. For information on how to deploy Management Agents on Microsoft Windows hosts using PsExec, see Appendix F.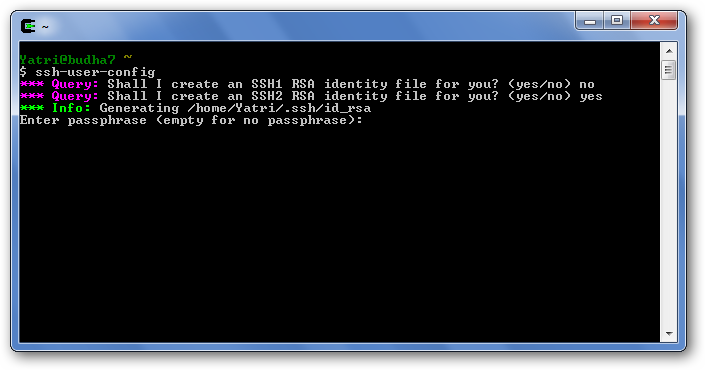

5.1About the Cygwin Requirement for Installing Management Agents
The Add Host Targets Wizard is an application built into the Enterprise Manager Cloud Control console. It offers GUI-rich, interactive screens that enable you to install Oracle Management Agents (Management Agents) on unmanaged hosts and convert them to managed hosts, so that they can be monitored and managed in Enterprise Manager Cloud Control.
When you use the Add Host Targets Wizard or EM CLI to install a Management Agent on a host running on Microsoft Windows, as a prerequisite, you must install Cygwin and start the SSH Daemon on the host. To do so, follow the steps listed in Section 5.3.
Cygwin is essentially a utility that offers a Linux-like environment on a Microsoft Windows host. Technically, it is a DLL (cygwin1.dll) that acts as a Linux API layer providing substantial Linux API functionality. Once you install Cygwin, you can configure the SSH Daemon on the host. The Add Host Targets Wizard is certified and supported with Cygwin 1.7.
The SSH Daemon enables the Add Host Targets Wizard to establish SSH connectivity between the OMS host and the host on which you want to install a Management Agent. Using this connectivity, the wizard transfers the Management Agent software binaries to the destination host over SSH protocol, installs the Management Agent, and configures it. Magic duels mac download.
5.2 Before You Begin Installing Cygwin
Before starting with the SSHD setup, ensure you are not using OpenSSH and MKSNT when using the Add Host Targets Wizard. To do so, perform the following checks:
Restart Ssh Aix
Ensure
OpenSSHbinandmksntare not in yourPATHenvironment variable. If they are, remove them by doing the following:Right-click on My Computer and go to Properties.
In the System Properties window, click Advanced.
In this tab, click Environment Variables.
Here, search for the
PATHsystem variable, select it, and if theOpenSSHbinandmksntare present inPATH,click Edit.In the Edit System Variable dialog box, delete these two values from
PATH,then click OK.
Stop the SSH Daemon if it is running from
OpenSSH,MKSor any other vendor. If the SSH Daemon is running, stop it by doing the following:Right-click on My Computer, and select Manage.
In the Computer Management window, in the left pane, expand Services and Applications, and select Services.
In the right pane, click the SSH Daemon/MKS Secure Shell service, then click the Stop button.
Note:
The navigational steps described in this section may vary for different Microsoft Windows operating systems.Restart Ssh Agent Mac
5.3 Installing Cygwin
To install Cygwin on a Microsoft Windows host, follow these steps:
Access the following URL, then click Install Cygwin:
Download the 32-bit version (if you are running a 32-bit version of Microsoft Windows) or the 64-bit version (if you are running a 64-bit version of Microsoft Windows) of the Cygwin setup executable.
Run the setup executable, then click Next to proceed.
On the Choose Installation Type screen, select Install from Internet, then click Next.
On the Choose Installation Directory screen, enter C:cygwin as the Root Directory, then click Next.
Note:
If you choose to install Cygwin in a different directory, then ensure that you update theSSH_PATH, SCP_PATH, MKDIR_PATH, SH_PATH, CHMOD_PATH, andTRUEproperties present in the$<OMS_HOME>ouiprovresourcesssPaths_msplats.propertiesfile to their proper Cygwin binary values, after installing the Enterprise Manager system.For example, if you choose to install Cygwin in the
D:softwarecygwindirectory, then update the specified properties in the following manner:On the Select Local Package Directory screen, select a directory on your local machine where you want to store the downloaded installation files, then click Next.
On the Select Connection Type screen, select appropriate settings to connect to the internet, then click Next.
On the Choose Download Site(s) screen, select any site from the available list, then click Next.
On the select packages screen, ensure that you select the following packages, then click Next:
From the Archive category, select
unzipandzipas follows:From the Net category, select
opensshandopensslas follows:After selecting the packages and clicking Next, the Resolving Dependencies screen is displayed. Click Next to proceed.
On the Installation Status and Create Icons screen, do not make any changes. Click Finish to complete the installation process.
5.4 Configuring SSH
This section describes how to configure SSH and test your Cygwin setup after installing Cygwin on a host.
Note:
While configuring SSH, you may need to run thecygwin.bat script. While running cygwin.bat in Microsoft Windows Server 2008 and Microsoft Windows Vista, ensure that you invoke it in administrator mode. To do this, right-click the cygwin.bat file and select Run as administrator.Restart Ssh Ubuntu
To configure SSH and test your Cygwin setup, follow these steps:
After you install Cygwin, navigate to the
C:cygwindirectory, open theCygwin.batfile in edit mode using any editor, and add the following line before invoking the bash shell.set CYGWIN=binmode ntsecFor example, here are the contents for the
Cygwin.batfile after adding the above line:To verify if Cygwin (
cygrunsrv)is installed properly, runC:cygwinCygwin.bat, and execute the following command:If Cygwin is installed properly, then all the Cygwin help options are displayed on the screen. However, if this command returns an error message, then you may have to reinstall Cygwin.
To configure the SSHD service, run
C:cygwinCygwin.bat, and execute the following command:After running the command, you are prompted the following questions:
At this point, if you want to use the same name, that is
cyg_server,enterno.You are then prompted the following questions:However, if you want to use a different name, enter
yes.You are then prompted the following questions:If the configuration is successful, you will see the following message:
Backup the
c:cygwinetcpasswdfile and then use any editor to open the file in edit mode. Remove only those entries of the user that you will use to connect to the host on which you want to install a Management Agent. Ask the user to make a backup of thec:cygwinetcpasswdfile before editing.If the user that you are employing to connect to the host on which you want to install the Management Agent is a local user, run
C:cygwinCygwin.batand execute the following:If the user you are employing to connect to the host on which you want to install the Management Agent running is a domain user, run
C:cygwinCygwin.batand execute the following:
(Only if the Cygwin software you have installed is of version 1.7.32 or higher) Open
C:cygwinetcsshd_configin a text editor and add the following line to the end of the file:KexAlgorithms diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha1,diffie-hellman-group1-sha1(For a domain user only) If the user you are employing to connect to the host on which you want to install the Management Agent is a domain user, do the following to start the SSH daemon:
Right-click on My Computer, and select Manage.
In the Computer Management dialog box that appears, go to Services and Applications, and select CYGWIN sshd.
Right-click CYGWIN sshd and select Properties.
In the Properties dialog box, go to the Log On tab.
Here, specify the domain/user name and password. Click Apply.
Run
C:cygwinCygwin.bat, and execute the following:Note:
If/var/log/sshd.logdoes not exist, you do not have to execute the following commands:
Perform one of the following steps to start the SSH daemon:
Run
C:cygwinCygwin.batand execute the following command:/usr/sbin/sshdOR
Run
C:cygwinCygwin.batand execute the following command:cygrunsrv -S sshdOR
Perform these steps:
Right-click on My Computer, and select Manage.
In the Computer Management dialog box that appears, go to Services and Applications, and select CYGWIN sshd.
Click CYGWIN sshd, then click the Start button.
Note:
If the SSH daemon does not start up, view thec:cygwinvarlogsshd.logfile for information on why the start up failed.You can now test your Cygwin setup.
To do this, go to a different machine (that has the
sshclient running), and execute the following command:For example,
This command will prompt you to specify the password. When you specify the correct password, the command should return the accurate date.
Note:
If you experience a process fork failure, memory leak error, or a file access error after configuring SSH, view the following website for a workaround:If you are unable to find a workaround for your problem, report your problem to the Cygwin community using the following website:
Restart Ssh Service Ubuntu
5.5 After Installing Cygwin and Configuring SSH
Restart Ssh
After installing Cygwin (as described in Section 5.3) and configuring SSH (as described in Section 5.4), follow these steps:
If the OMS host runs on a Microsoft Windows platform, perform the following on the OMS host:
Right click My Computer, then select Properties. In the window that appears, select Advanced system settings, then select Environment Variables. In the System Variables section, create the
CYGWINvariable, and specify its value asnodosfilewarningNote:
You do not need to restart the host after performing this step.Navigate to the Cygwin install directory (that is,
C:cygwinif you chose to install Cygwin in the default location), open theCygwin.batfile in edit mode using any editor, then edit the following line:For example, these are the contents of the
Cygwin.batfile after editing the above line:From the Start menu, select Run. For Open, enter
services.msc,then click OK. Search for the Cygwin SSHD service and stop it.Navigate to the Cygwin install directory (that is,
C:cygwinif you chose to install Cygwin in the default location), then runCygwin.bat.Run the following command to start the SSHD service:Free download pdf to word for mac. Note:
Running this command may return an error mentioning that/var/emptymust be owned by the root user. If you encounter this error, run the following from the Cygwin terminal:After running this command, retry the
$ /usr/sbin/sshdcommand.
Perform the tasks mentioned in Step 1 on all the Microsoft Windows target hosts (on which you want to install Management Agents using the Add Host Targets Wizard or EM CLI).
